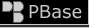





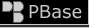 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
This image shows the unstable LBV star Eta Carinae surrounded by the Homunculus Nebula, two mushroom-shaped clouds ejected by the star, each of which is hundreds of times larger than our solar system.
A considerable expansion of the nebula is visible when comparing the images above. The gas in the nebula is known to have been ejected from the star at speeds of up to 2000 km/s.
This, the most luminous star known in our Galaxy, is 100 times more massive than our Sun and 5 million times as luminous. The star has entered the final stage of its life and is highly unstable. It undergoes giant outbursts from time to time, with the Homunculus Nebula being the result of the most recent in 1841. At that time, and despite its large distance of 7,500 light-years - Eta Carinae briefly became the second brightest star in the night sky, surpassed only by Sirius.
It is believed that Eta Carinae may explode as a spectacular supernova within the next few thousand years.
Details are:
10” Newton / ToUCam Pro SC1
Televue 5x Powermate
Combined exposures: 1046 x 1/25s, 1811 x 0.75s, 200 x 2.75s all unfiltered and finally 111 x 1.0s with OIII filter.
Copyright Rolf Wahl Olsen 2011
| gazon | 26-Jun-2015 15:50 | |